Class preference regarding lab grade
Ψlogical
Testing
…infants & other special populations
🐾🐾🛁 cleaning up 🧼🐾🐾
- corrected syllabus now in Canvas
Project:
- more items & platform decision
- Qualtrics?
- special populations?

![]()
Class survey results 📈📉
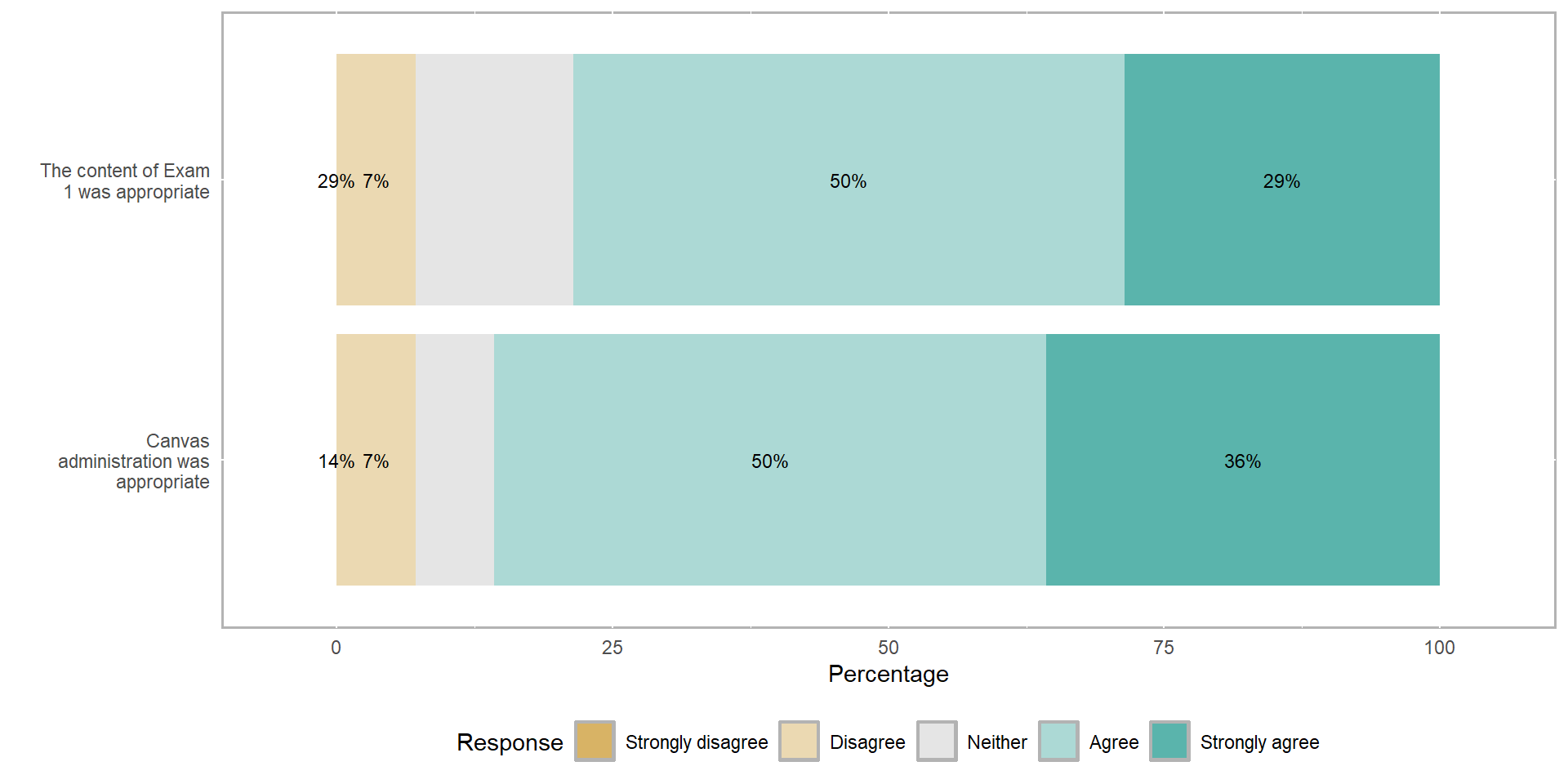
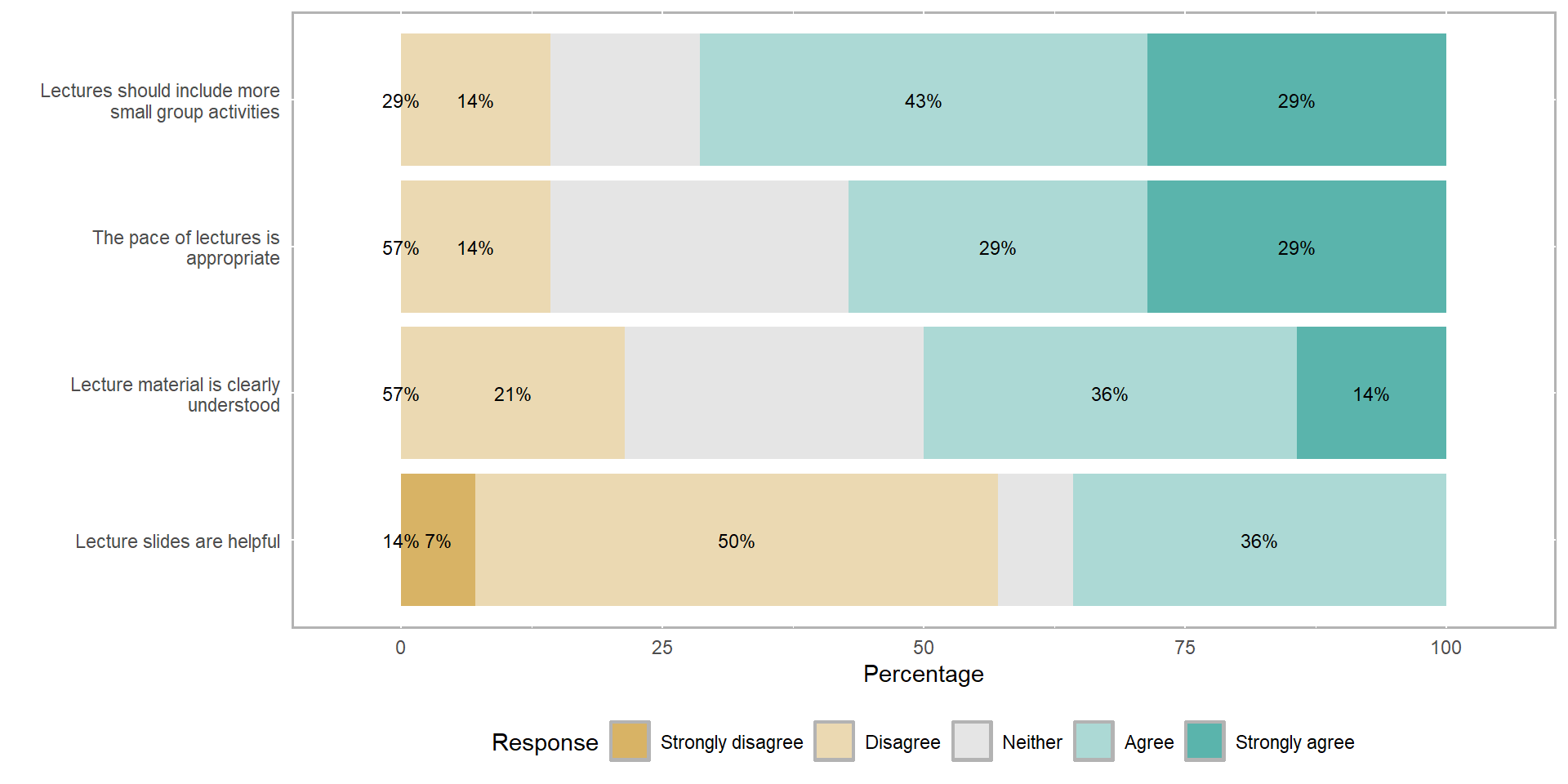
“I, and a few of my classmates, would rather we not take the 30 min break before lab and instead finish class 30 mins early because this is a late class.”
“There was much more crystalized knowledge than I expected (names, dates, acronyms) that usually don’t show up on tests. I tend to feel that tests with applicable knowledge based questions (fluid) allow me to retain information better.”
“I can tolerate having exams on canvas (I know it makes the grading process easier), but I don’t love it and having a paper option would be nice.”
“Lecture is too slow”
“Hard to differentiate some times what material is related to exam items and what is unnecessary information, makes preparing for exams difficult.”
“It is difficult to know what we should be studying in prep for the exam. Could you provide a study guide or quizlet?”
“I understand this takes more work on your part, but it would be nice to have a study guide/outline before exams if you are willing.”
“Alternative” ability measures
…to the Binet & Wechsler tests
- special populations or purposes
- age
- disability
- language
- content
Note
typically less dependent on literacy or reading ability

Early “nonverbal ability” tests (I)
- Seguin Form Board Test (Seguin, 1907)
- 1866 – predates Binet
- still commercially available
Note
This test was an evaluation of mental retardation – not typically considered an intelligence test

Early “nonverbal ability” Tests (II)
- Healy–Fernald Test (Healy & Fernald, 1911)
- criminality
- puzzle–based
- “adolescent delinquents”

Early “nonverbal ability” Tests (III)
- Knox Cube Imitation Test (Knox, 1914)
- Ellis Island
- cube test just one of several
- battery
- still available

Infants!!!
Why?!?
- developmental delays
- concerning behavior
- mental retardation
Warning
textbook authors’ equivocation should not implicate any of these as purported intelligence tests

Brazelton Neonatal Assessment Scale (BNAS)
- newborn response to new environment
- 3 days \(\rightarrow\) 4 weeks–old
- ~50 “scores”
- no overall aggregate
Gesell Developmental Schedules (GDS)
- several revisions since Gesell (1925)
- 2.3 months \(\rightarrow\) 6.3 yo
- norms of developmental stage attainment
- “development quotient” similar to Mental Age

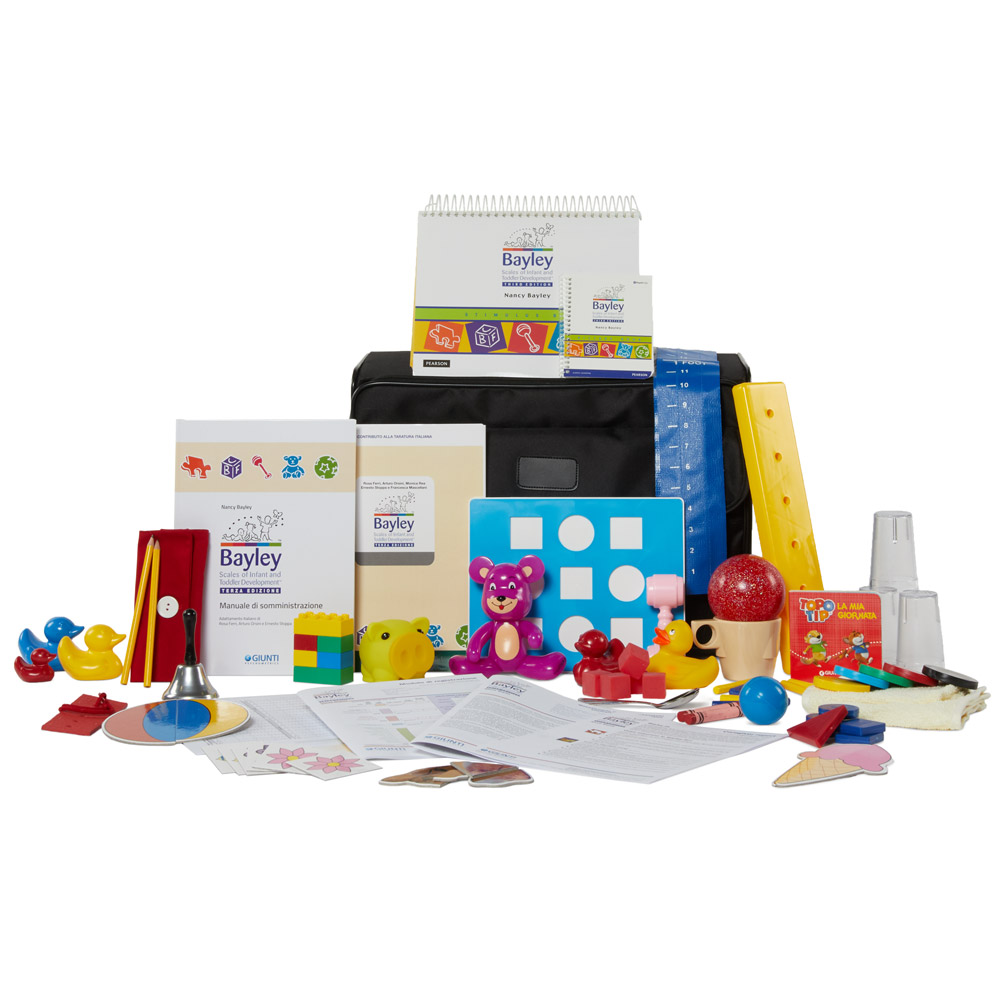
Bayley Scales of Infant Development (BSID)
- 1 \(\rightarrow\) 42 months
- several revisions since Bayley (1969)
- normed (like GDS) but with larger stratified sample
Note
4th edition actually most current (see example feedback report)

Cattell Infant Intelligence Scale (CIIS)
- 2 \(\rightarrow\) 30 months
- DOES purport to measure intelligence (Cattell, 1940)
- not available as of 2015
Note
Psyche Cattell was the daughter of James Cattell but unrelated to Raymond B Cattell of gf and gc fame

Young Children

McCarthy Scales of Children’s Abilities (MSCA)
- 2 \(\rightarrow\) 8 yo
- McCarthy (1972)
- General Cognitive Index (GCI)
- akin to g
- not available as of 2015

Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children (KABC)
- 3 \(\rightarrow\) 18 yo
- 18 subtests, 5 scales
- Sequential–simultaneous distinction
- serial vs. parallel problem–solving
- original (Kaufman & Kaufman, 1983) & 2004 revision (KABC-II)

Special Populations
- Columbia Mental Maturity Scale (CMMS)
- cerebral palsy 3 \(\rightarrow\) 12 yo
- Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test (PPVT-IV)
- physical or language handicap 2 \(\rightarrow\) 90 yo
- Leiter Internatinoal Performance Scale
- autistism or cognitive impaired 2 \(\rightarrow\) 20 yo
- Porteus Maze Test (PMT)
- planning & flexible problem–solving
Learning disabilities

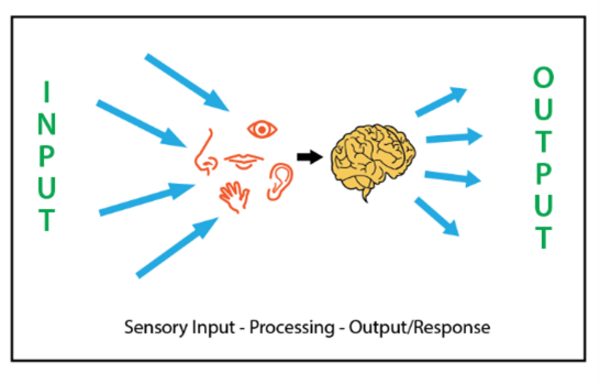
Illinois Test of Psycholinguistic Abilities (ITPA)
- 5 \(\rightarrow\) 12 yo
- input can be visual, auditory, or tactile
- 12 subtests measure ability to receive these inputs
- 3 “global” composites
- general, spoken, & written language
Woodcock–Johnson
- actually 3 different batteries
- Tests of cognitive abilities
- Tests of achievement
- Tests of oral language
Note
Can be used together or separately – if together, discrepancy between ability & achievement might indicate a learning disability
![]()

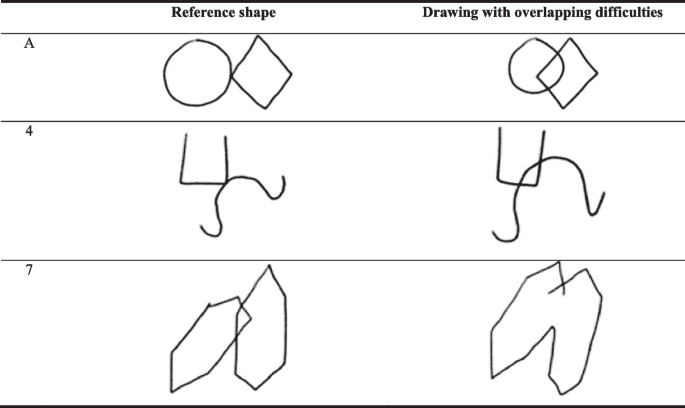
Visiographic tests
typically applied in contexts where brain damage is suspected
creativity tests…
…have historically been very tricky to develop
- Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT)
- fluency – number of solutions
- originality – novelty of solutions
- flexibility – try new approaches
- original (Torrance, 1966) has been revised at least 5 times

Achievement and ability should be considered unique (e.g., meaningfully different) terms
- True
- False
Several tests grouped together for purposes of “whole–person” assessment comprise a test __________
- battery
- cluster
- bunch
- galaxy
“Ability” tests that ask respondents to manipulate physical objects are sometimes referred to as ____________ tests
- nonverbal
- verbal
- physical
- physiological
___________ scales on ability tests may ask respondents to manipulate physical objects
- performance
- scaled
- standardized
- raw score
These tests ask respondents to recreate drawn shapes…
- visiographic
- pictographic
- intelligraphic
- isographic

