4 Implementation of soil health practices for mitigating climate change in Africa
4.1 Implementation frameworkImplementation plan
4.1.1 Implementation plan
The implementation plan focuses on developing the roadmap for a smooth and efficient roll-out of the soil health practices for mitigating climate change at different levels in Africa. The plan entails three main steps (Figure 4.1):
- Step 1: selecting the appropriate implementation level
- Step 2: initial preparation for implementation
- Step 3: designing implementation frameworks
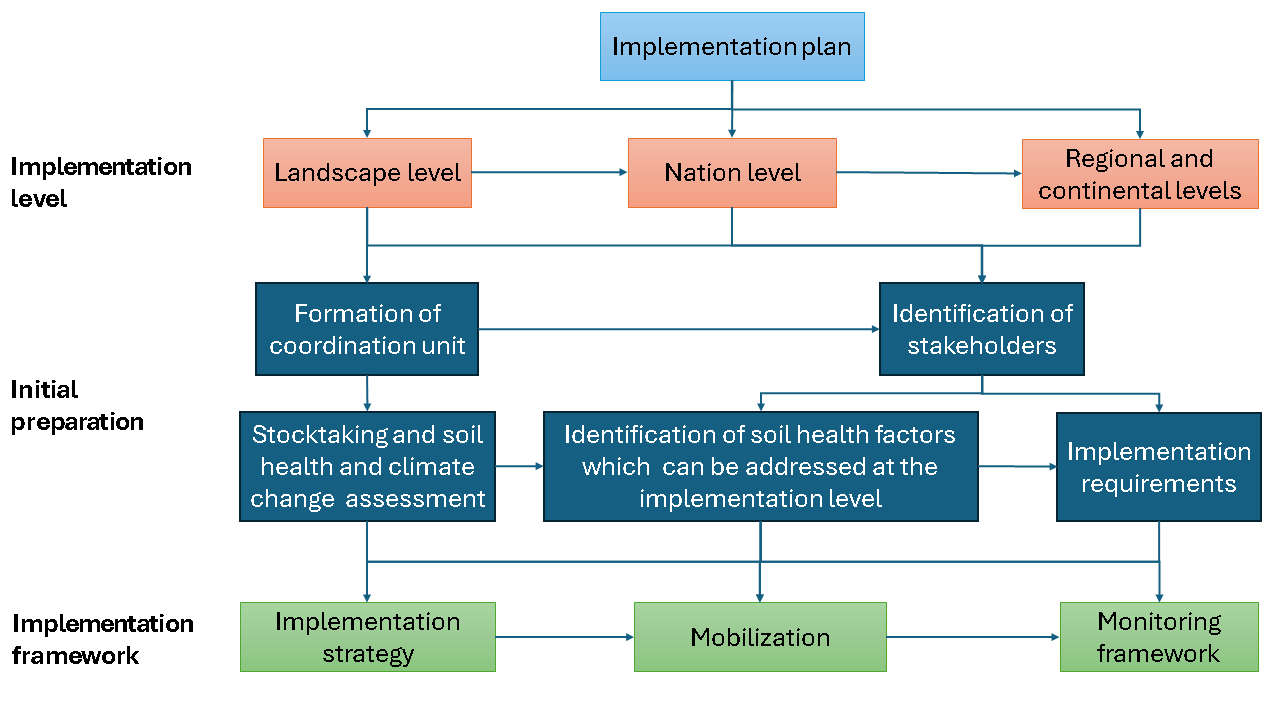
Figure 4.1: Implementation plan for soil health to mitigate climate change in Africa
The choice of implementation level in step 1 guides the activities to be prioritized at that level. For example, while the landscape level remains the lowest level for implementation of soil health practices for mitigating climate change, higher levels like national, regional and continental levels can deal with soil health factors that need policy, regulatory, standardization, and coordination actions. The choice of implementation level is followed by initial preparation in step 2, which includes the establishment of a coordination unit and the identification of stakeholders to support the implementation process. The coordination unit and stakeholders will design and carry out stocktaking and assessment of climate change and status of soil health, identification of factors of soil health to tackle at the selected implementation level, and determination of soil health implementation requirements in Challenges with soil health practices for mitigating climate change in Africa. The last step entails the development of an implementation framework which includes implementation strategy, mobilization of human, financial and institutional resources needed to implement the plan, and monitoring and evaluation aspects.
The implementation plan also portrays the relationship and synergy between different implementation levels (landscape, national, regional and continental) to maximize success and impacts of soil health practices for mitigating climate change in Africa. The relationship is manifest in the way different levels identify the soil health factors to prioritize, the stakeholders between and within the levels, and coordination and communication between the levels.
4.1.2 Implementation framework
The implementation framework provides the structure for carrying out soil health management to mitigate climate change at any of the planned implementation levels. The framework is envisaged in three phases to provide room for accomplishing the implementation in sizeable and manageable chunks.
Phase 1: Situation analysis and strategies for gap-filling
Phase 1 of the framework is concerned with analysis of the situation, identifying gaps and strategies for gap filling. It focuses on soil health and climate change assessment to determine bright and hotspot areas in the landscape for prioritization (Figure 4.2). It also includes resource-needs assessment and assessment of human and institutional capital. These assessments are necessary to develop a suitable sustainability plan.
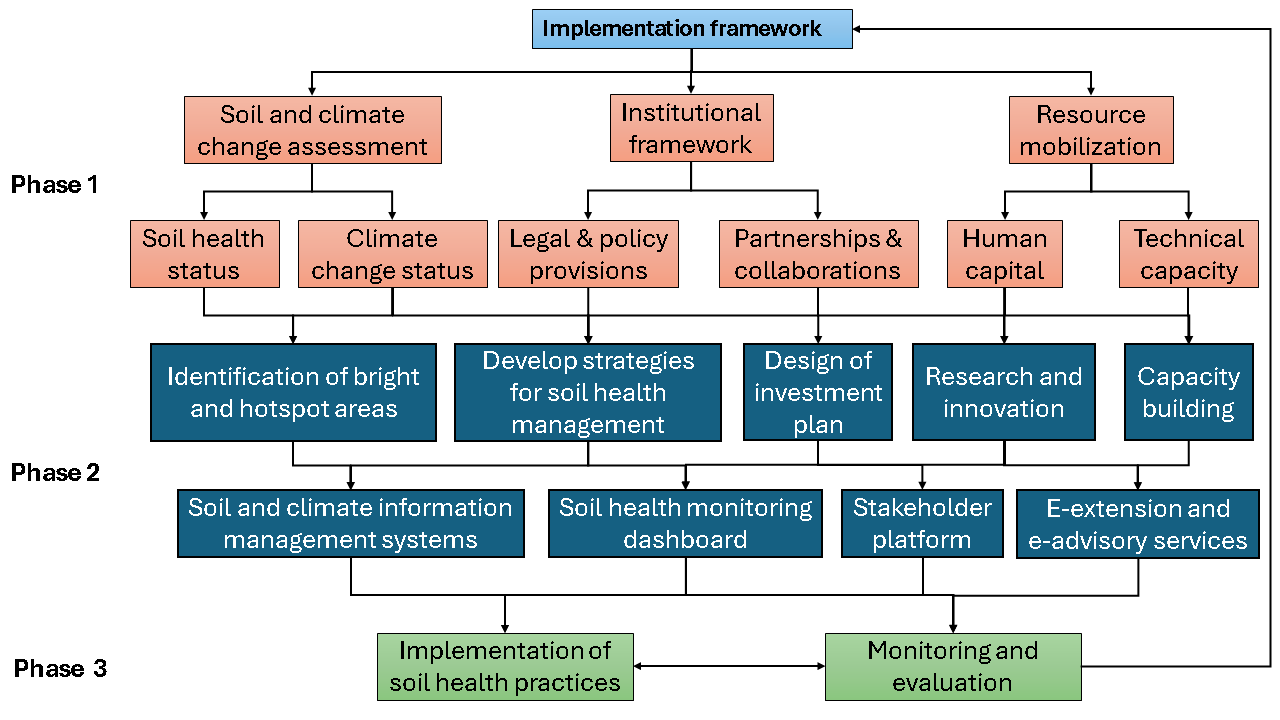
Figure 4.2: Implementation framework for soil health management to mitigate climate change
Phase 2: Development of implementation tools
Phase 2 of the implementation framework integrates the outputs of phase one to develop implementation tools such as soil and climate information management systems, soil health monitoring dashboard, stakeholder platform, and decision support (e-advisory and e-extension tools). The implementation tools are also useful in tracking policy impacts on soil health and trigger for improvements.
Phase 3: Implementation and monitoring
Actual implementation of designed strategies and soil health occurs in phase 3. Soil health practices for mitigating climate change are implemented at the landscape level while other strategies (such as national strategies for promoting soil health, regional or continental agreements on soil health, etc.) are recommended for other, higher levels of implementation.
4.2 Monitoring framework
4.2.1 Monitoring plan
Monitoring implementation of soil health practices for mitigating climate change should consider the target objectives at different implementation levels. The plan is to integrate the monitoring framework with the CAADP monitoring and evaluation system. The plan also seeks to identify key indicators which are easily determined and carry the necessary information to track implantation progress. Table 4.1 summarizes key considerations that should be prioritized when planning monitoring of implementation of soil health strategies to mitigate climate change.
| Level | Objective | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Landscape level | Increasing resilience to climate change | Increase rate of adoption of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) |
| Reducing GHG emissions | Technological advancements | |
| Information access and awareness level | ||
| Reducing soil degradation | Extent and rate of degradation | |
| Proper planning and prioritization | ||
| National level | Providing institutional support | Policy, legal, and coordination support |
| Financial support and partnerships | ||
| Standardization and regulation of soil health practices | ||
| Providing technical support | Capacity building, promotion, awareness | |
| Information access and advisory services | ||
| Regional and continental levels | Promoting climate-smart decisions in agriculture | Policy support and awareness raising programs |
| Prioritizing soil health | Strategies for incorporating soil health in development agenda | |
| Mitigating climate change |
4.2.2 Indicator monitoring
Indicators for monitoring implementation of soil health for mitigating climate depends on the level of implementation. Using the implementation plan factors in Table 4.1, the following indicators have been proposed for monitoring and reporting the progress of implementation of soil health strategies for mitigating climate change in Africa (Figure 4.3):
- Spatial distribution of soil carbon stocks and degradation
- Number of CSA technologies being implemented
- Number of policies and legislation for promoting CSA
- Budgetary allocation for CSA at the national level
Where applicable, these indicators can be integrated into CAADP monitoring and evaluation program.
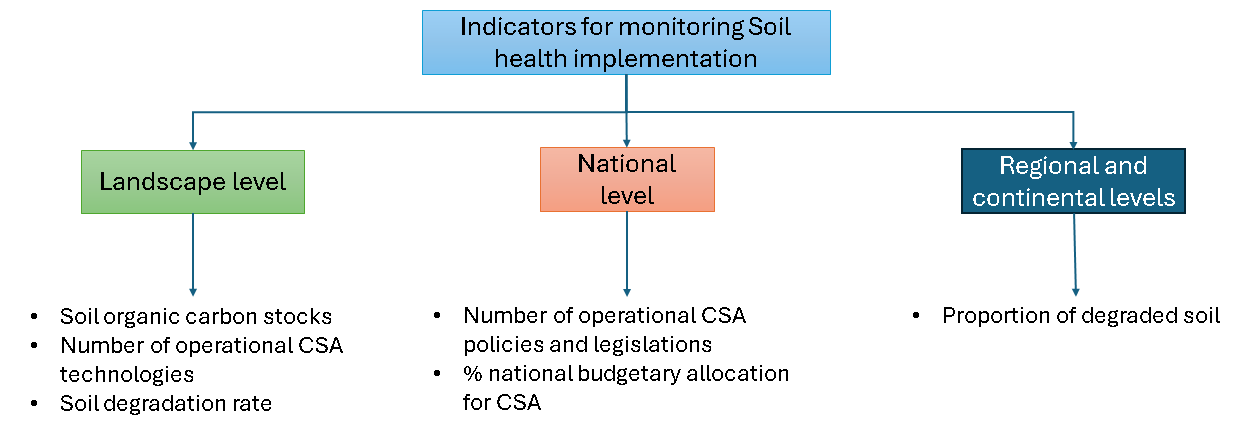
Figure 4.3: Implementation Framework